The study of the interactions between organisms the environment Biology Diagrams Understanding this flow is crucial for comprehending how ecosystems function, how organisms interact, and how environmental changes can impact ecological balance. This article aims to study in detail the concepts related to Energy Flow in Ecosystem, including Food Chain, Food Web, Trophic Levels, Ecological Pyramid among others.
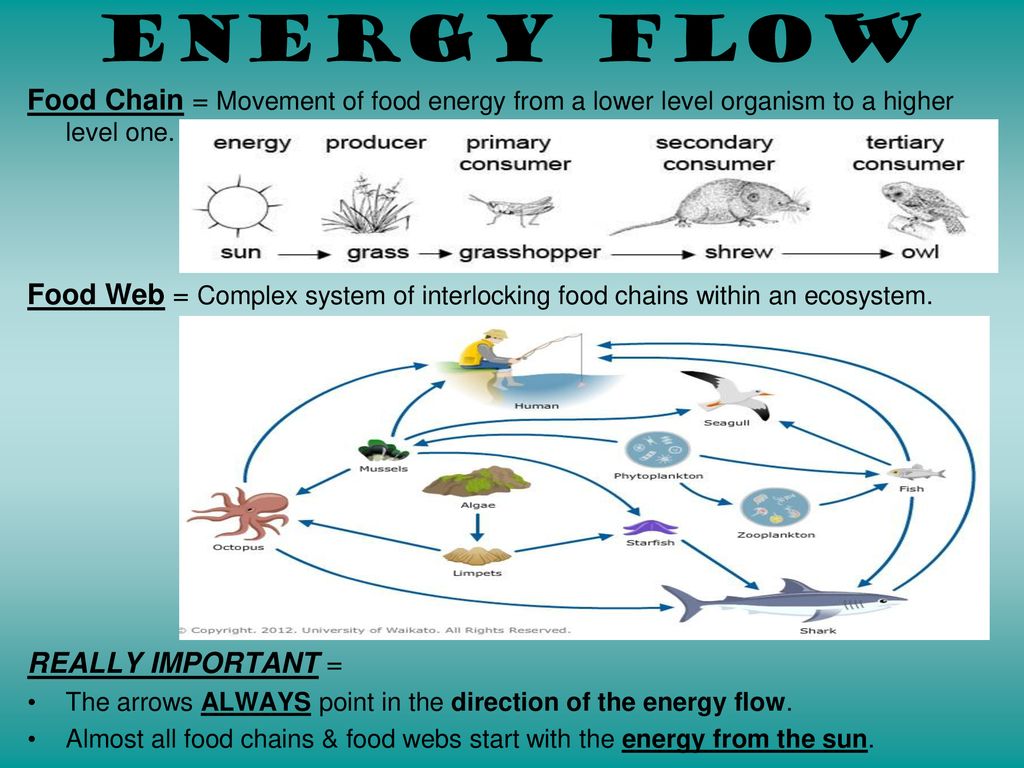
What Are Food Webs? While a food chain illustrates a simple path of energy flow, a food web is a more complex representation of the interconnected food chains in an ecosystem. A food web consists of multiple food chains that are interconnected and overlap, reflecting the fact that most organisms consume more than one type of food.

Importance of Food Chains In The Energy Flow In The Ecosystem Biology Diagrams
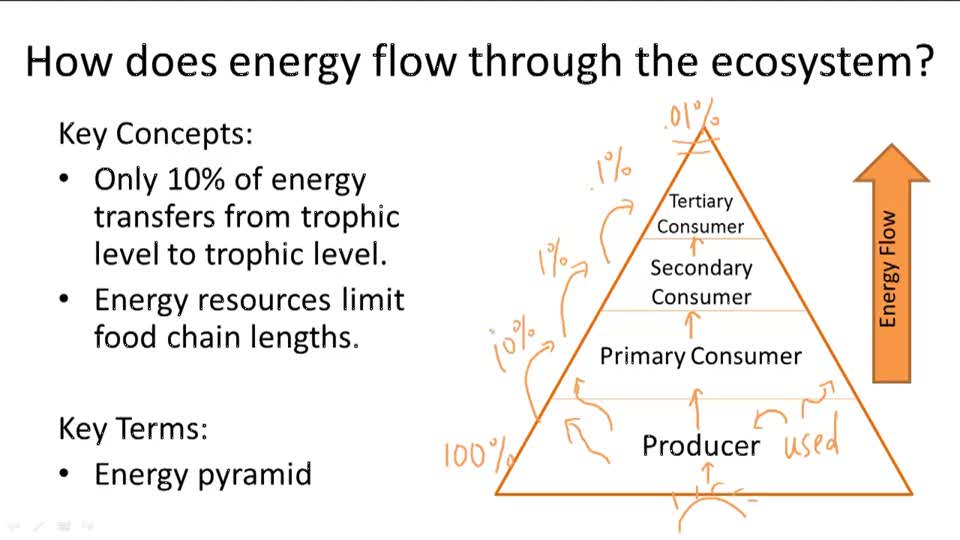
The definition of energy flow is the transfer of energy from the sun and up each subsequent level of the food chain in an environment. Each level of energy flow on the food chain in an ecosystem is designated by a trophic level, which refers to the position a certain organism or group of organisms occupies on the food chain.
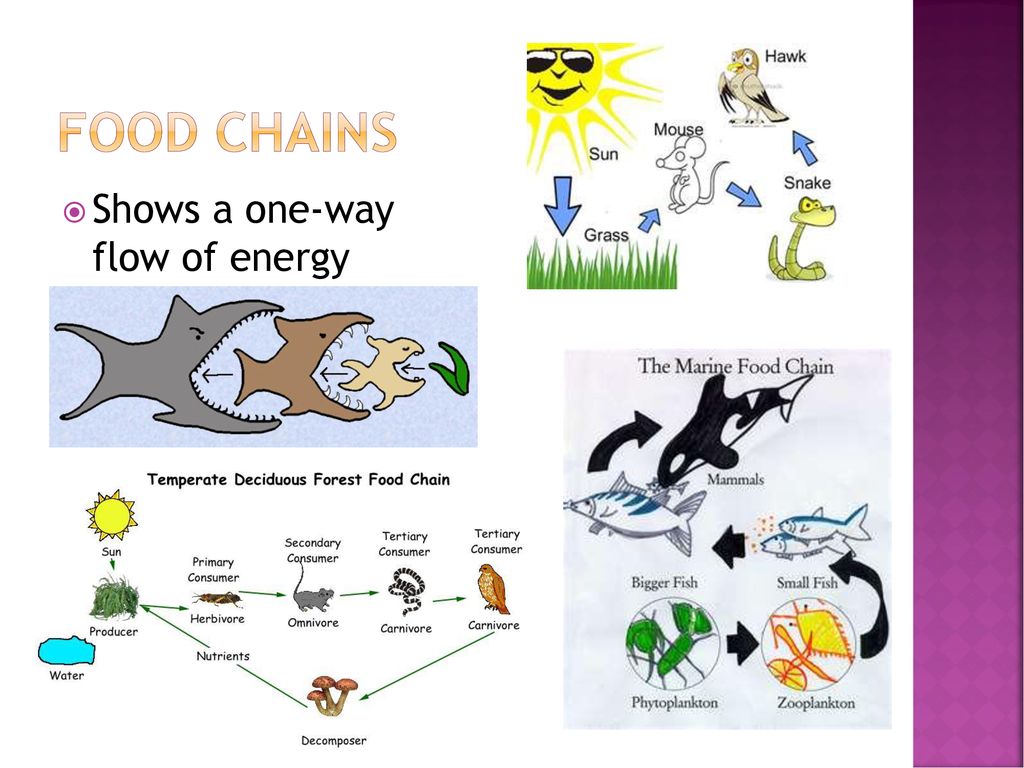
The flow of energy in an ecosystem is always linear ie uni direction; At each energy step in food chain, the energy received by the organisms is used for its own metabolism and maintenance. The left over energy is passed to next higher trophic level. Thus the energy flow decreases with successive trophic level. Flow of energy follows the This reduction in energy flow is visually depicted in Figure 2, which shows the energy flow in a linear food chain with three trophic levels. Each trophic level is represented by a box, with the size of the box indicating the amount of energy stored as biomass. The pipelines connecting the boxes represent the energy flow in and out of each

Food Chains and Food Webs: Energy Flow in Ecosystems Biology Diagrams
Natural Disasters: Events like floods, fires, volcanic eruptions, or droughts can drastically alter habitats, destroying food sources or killing off organisms within a food chain. Disease: Disease outbreaks can decimate populations at specific trophic levels, disrupting energy flow. Population Fluctuations: Natural predator-prey cycles or seasonal changes in resource availability can cause